Cannabis cultivation, whether for personal use or for the burgeoning legal market, can be a deeply rewarding and therapeutic experience. However, it comes with its own set of challenges, particularly when it comes to pests. Insect and pest management is a crucial aspect of successful cannabis cultivation, and with the increasing emphasis on organic and sustainable practices, it's important to adopt a responsible approach. In this blog, we'll explore the potential pests that can affect your cannabis plants and provide evidence-based guidance on establishing an effective insect and pest management program, including the use of biocontrols.
Common Cannabis Pests
Aphids (Aphidoidea): These tiny, soft-bodied insects can quickly multiply and infest cannabis plants. They feed on the plant's sap, causing wilting and leaf damage.
Spider Mites (Tetranychidae): These arachnids are notorious for their ability to inflict serious damage. They suck the chlorophyll from plant cells, leading to yellowing leaves and reduced growth.
Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae): Whiteflies are small, winged insects that feed on cannabis leaves. They excrete a sticky substance called honeydew, which can attract sooty mold and other pests.
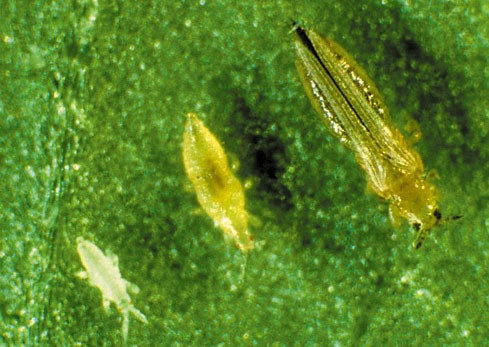
Thrips (Thripidae): Thrips are slender, winged insects that scrape plant cells and feed on the contents, leading to a stippled appearance on leaves.
Fungus Gnats (Sciaridae): Fungus gnats primarily affect the root system, with larvae consuming plant roots, while adults can damage young plants.
Caterpillars (Various Families): Caterpillars, such as armyworms and budworms, can chew through leaves and buds, causing extensive damage.
Powdery Mildew (Podosphaera spp.): This fungal pathogen creates a white, powdery growth on leaves, inhibiting photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Establishing an Insect and Pest Management Program
Start with Preventative Measures:
Cleanliness: Maintain a clean growing environment to reduce pest attraction. Regularly remove dead or decaying plant material.
Quarantine: Inspect new plants for pests before introducing them to your garden.
Healthy Soil: Use high-quality organic soil to promote strong plant growth, which can withstand pest attacks.
Use Beneficial Insects:
Ladybugs (Hippodamia spp.): These voracious predators feed on aphids and other soft-bodied pests.
Predatory Mites (Phytoseiulus spp.): Effective against spider mites, these tiny mites can maintain mite populations at a manageable level.
Parasitic Wasps (Encarsia spp., Eretmocerus spp.): These wasps parasitize whiteflies and help control their numbers.
Neem Oil and Insecticidal Soaps:
Neem oil and insecticidal soaps are organic and effective treatments for a variety of pests. They work by disrupting the pests' physiology and lifecycle.
Diatomaceous Earth:
Dust your plants with food-grade diatomaceous earth to create a physical barrier that damages the exoskeleton of crawling pests.
Companion Planting:
Certain companion plants, like marigolds, can help deter pests by emitting natural repellents.
Beneficial Nematodes:
These microscopic roundworms can be used to control soil-dwelling pests like fungus gnats.
Regular Monitoring:
Inspect your plants regularly to catch pest infestations early. Early intervention is often more effective.
Use yellow sticky cards to monitor pests and check daily.
Successful cannabis cultivation requires a proactive approach to pest management. By focusing on organic and sustainable solutions, such as beneficial insects, neem oil, and companion planting, you can protect your plants without resorting to harsh chemicals. Remember that pest management is an ongoing process, and staying vigilant is the key to a thriving cannabis garden. Experiment with different methods and find what works best for your specific growing conditions. With the right approach, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest while maintaining the health and vitality of your cannabis plants.














Comments